TL;DR
Introducing tdm, a CLI tool that automates technical debt discovery, triage, and resolution. tdm transforms technical debt management into a proactive, automated process that works seamlessly with your existing development tools through MCP integration.
Source code: https://github.com/NikiforovAll/tech-debt-master
- TL;DR
- Motivation
tdmworkflow- Let’s Get Started
- Technical Debt Discovery
- Triaging Technical Debt
- Technical Debt Resolution
- References
Motivation
As software development continues to evolve, one thing remains constant: technical debt accumulates faster than we can manage it.
This is where Technical Debt Master (hereafter tdm) comes in. With the emergence of local/open-weights LLMs like DeepSeek R1 and GPT-OSS models that can run through tools like Ollama or LM Studio, we now have an unprecedented opportunity to bring AI-powered code analysis directly to our development environments.
But the advantages of using local LLMs for code analysis are compelling:
- Privacy and Security: Your code never leaves your environment
- Cost Efficiency: No API costs for analysis runs
- Offline Capability: Work without internet connectivity
- Control: Full control over model versions and behavior
Another compelling reason to use tdm in automation. Instead of relying on developers to remember which parts of the codebase need attention or hoping that code reviews will catch accumulating problems, tdm transforms this reactive approach into a proactive, automated system that works alongside your existing development workflow. More importantly, you catch architectural problems and code quality issues before they become expensive to fix, fundamentally shifting the cost curve in your favor.
tdm workflow
tdm implements a structured, phase-based approach to technical debt management:
- Phase1️⃣ - Discovery. Continuous scanning identifies new technical debt as it’s introduced and AI-powered analysis provides context and severity assessment.
- Phase2️⃣ - Triage. This stage offers two workflows: interactive CLI for individual developers to review and prioritize issues directly in the terminal, or HTML reports for team-based collaborative sessions where developers can discuss priorities together.
- Phase3️⃣ - Resolution. The resolution stage leverages MCP server to enable automated technical debt remediation. Once triaged, identified technical debt items are exposed through the MCP server, effectively creating a structured backlog that AI coding agents can consume and act upon. This approach provides great flexibility - you can integrate
tdmwith your existing AI tools such as GitHub Copilot, Cursor, Claude Code CLI, Gemini CLI, etc.
Let’s Get Started
Installation
Install tdm from source code:
dotnet cake --target pack
dotnet tool install --global --add-source ./Artefacts TechDebtMaster.Cli
You can use tdm help to get a helpful reference for all available commands.
tdm help
# Available Commands:
# Repository Management
# repo Repository management and indexing operations
# ├─ index [path] Index repository content
# └─ status [path] Show status of previous analysis and repository changes
# Debt Analysis
# debt Technical debt analysis and reporting
# ├─ analyze [path] Perform debt analysis on all indexed files
# ├─ show [path] Show technical debt statistics in a tree structure grouped by tags
# ├─ view [path] View detailed content of specific technical debt items
# ├─ report [path] Generate an interactive HTML report of technical debt
# └─ import [report-file] Import modified HTML report to update analysis data
# System Management
# init Initialize tdm in the current repository
# config Manage configuration settings
# ├─ show Display current configuration
# └─ set [key] [value] Set a configuration value
# prompts Manage prompt templates
# ├─ edit Edit a prompt template
# ├─ restore Restore prompt templates to default state
# └─ set-default Set the default prompt template
# mcp Start Model Context Protocol server
# clean Remove the .tdm folder from the current directory
# help Show this detailed help information
Configuration
You can manage tdm configuration settings using the tdm config command. This allows you to customize various aspects of the tool to better fit your needs.
tdm integrates with OpenTelemetry to export detailed telemetry data including token consumption, model inference times, and per-analysis cost breakdowns, providing precise visibility into codebase analysis costs. In this blog post I will use it in conjunction with the .NET Aspire Dashboard. Also, we will use Aspire to work with Ollama to deploy local LLM models.
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var ollama = builder
.AddOllama("ollama")
.WithImageTag("0.6.0")
.WithOpenWebUI(ui => ui.WithImageTag("0.5.20"))
.WithDataVolume()
.WithLifetime(ContainerLifetime.Persistent);
var r1 = ollama.AddModel("deepseek-r1", "deepseek-r1:1.5b");
// (alternatively) if you have free 16GB of RAM you can try something like
var gpt = ollama.AddModel("gpt-oss", "gpt-oss:20b");
// (optional) we use it to get a connecting string and otel configuration
builder
.AddProject<Projects.TechDebtMaster_Cli>("tdm")
.WithArgs("--", "help")
.WithReference(r1);
builder.Build().Run();
Now, we can run it using Aspire CLI:
aspire run
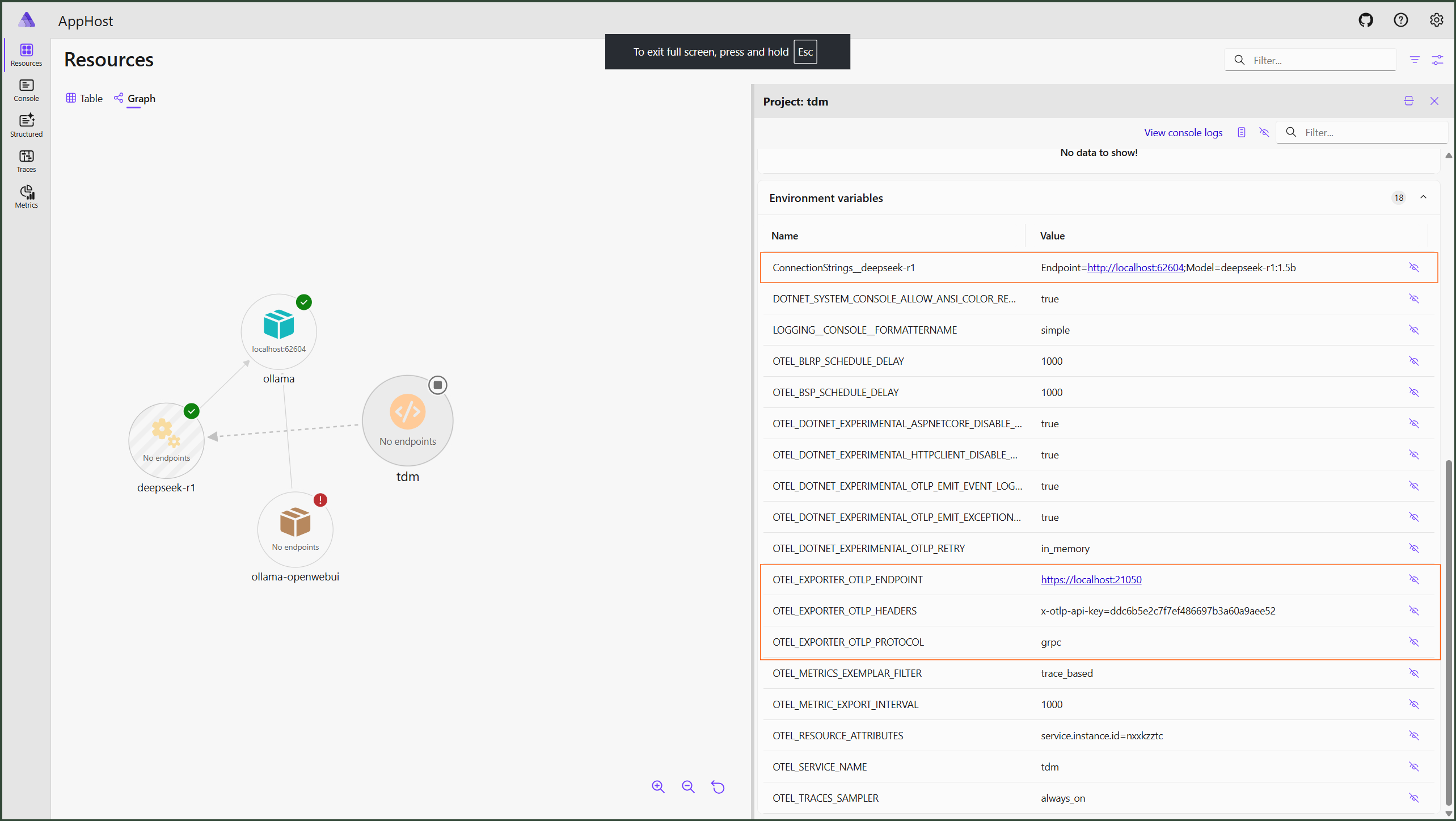
Now we can configure tdm:
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT=https://localhost:21050
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS=x-otlp-api-key=ddc6b5e2c7f7ef486697b3a60a9aee52
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL=grpc
tdm config set ai.provider ollama
tdm config set ai.url http://localhost:62604
tdm config set ai.model 'deepseek-r1:1.5b'
tdm config set default.include '\.cs$' # we will use it with C# code base, so it makes sense to analyze only C# files
The beautiful part about tdm is that you can customize analysis prompts to better fit your project’s needs. Run tdm prompts edit to open the prompt in your default system editor.
💡 For example, you can configure tdm to identify specifically security-related issues by creating dedicated security.prompty file. tdm leverages Prompty for prompt management.
Technical Debt Discovery
Initialize tdm and index the repository with technical debt. In our case it is called tdm-testproject-monkeymcp (some project with technical debt)
tdm init
# √ Updated .gitignore to include .tdm folder
# √ TechDebtMaster initialization complete!
tdm repo index
# Analyzing repository: .
# Include pattern (from default.include): \.cs$ (only files matching this pattern will be analyzed)
# √ Repository analyzed successfully!
tdm repo status
# Analysis Status for: .
# Last analyzed: 2025-08-09 15:53:45 UTC
# Recent Changes:
# New files (6):
# + MonkeyMCP/Program.cs
# + MonkeyMCPShared/MonkeyPrompts.cs
# + MonkeyMCPShared/MonkeyResources.cs
# + MonkeyMCPShared/MonkeyTools.cs
# + MonkeyMCPSSE/Program.cs
# ... and 1 more
Now we are ready to perform technical debt analysis for the configured prompt using.
tdm debt analyze
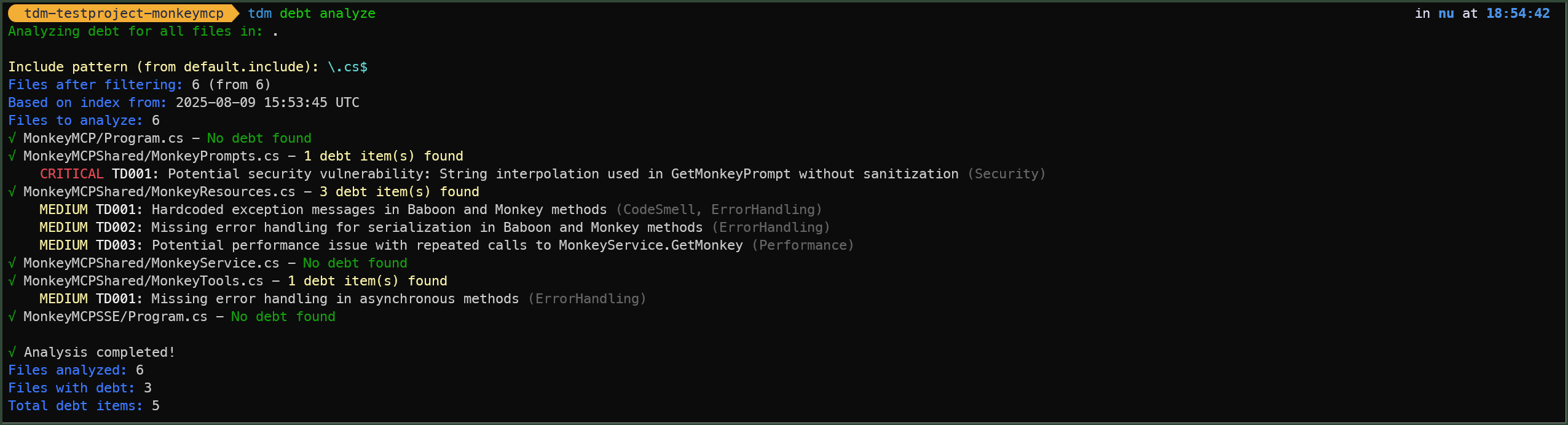
Here is an example of data we can find in the Aspire Dashboard, each command has a separate trace:
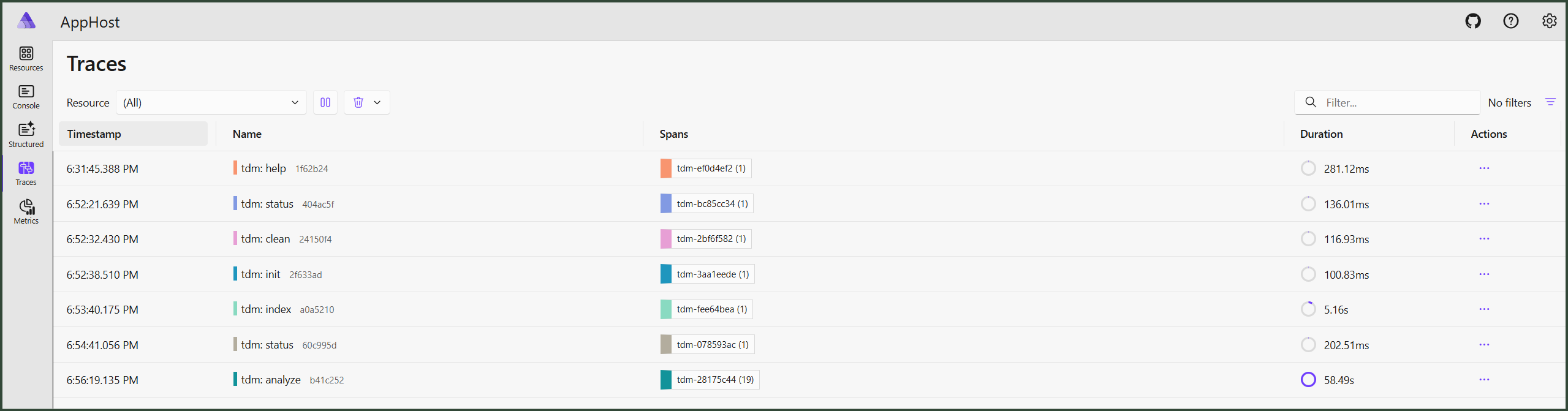
💡 Each command has a separate trace
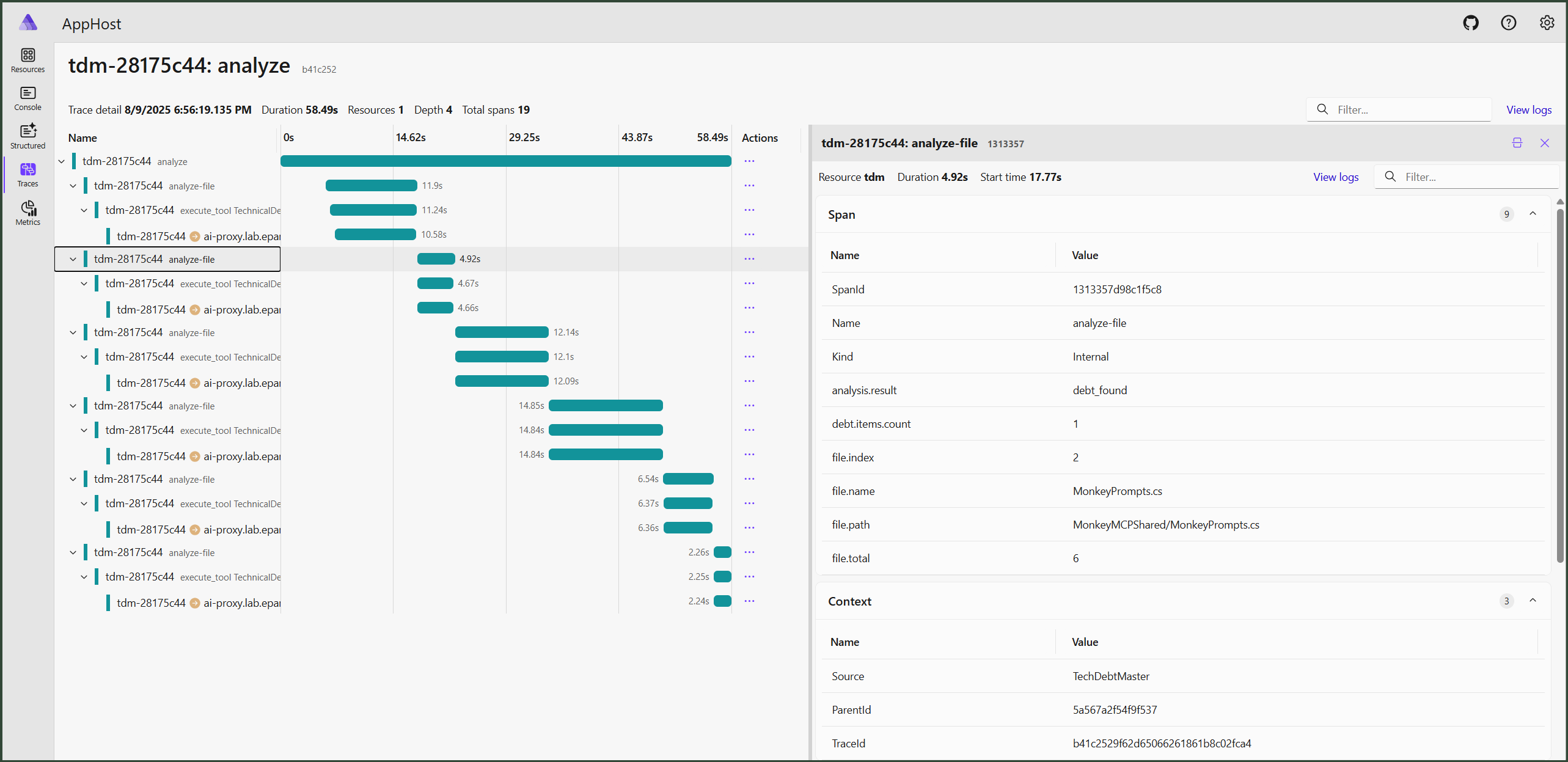
💡 You can drill down to see individual traces for find per-file analysis traces.
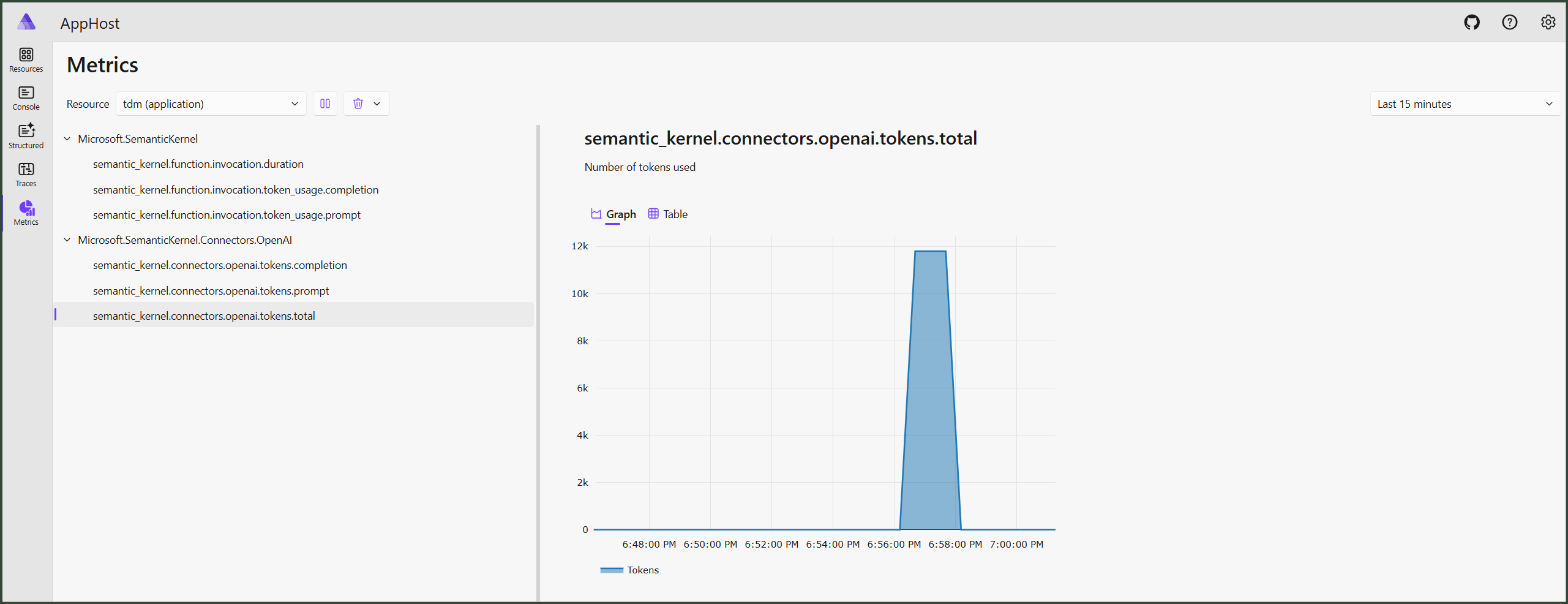
💡 Metrics give you insights into the overall LLM usage.
Once we have a backlog of technical debt identified, we can prioritize and address it effectively.
Triaging Technical Debt
Triaging technical debt means prioritizing identified issues based on business impact and remediation effort. tdm enables effective team triaging through structured reports where developers can collaboratively assess technical complexity against business priorities.
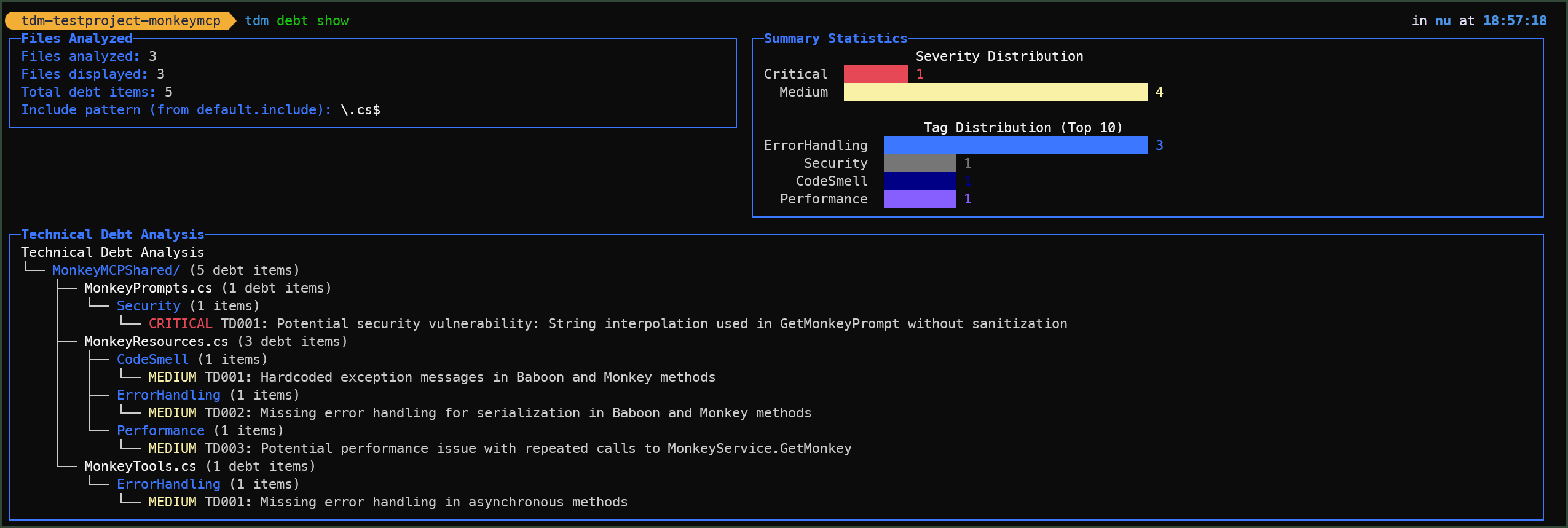
Use tdm debt show to get a tree view of technical debt items:
tdm debt show
You can work with items using tdm debt view --interactive command:
tdm debt view --interactive
💡 In the demo above, I showcased how to interactively view, manage, and export backlog items in various formats. For example, using --xml can be useful if you prefer not to use MCP and instead want to export backlog items in a more portable format. Similarly, a command like tdm debt show --json would also work.
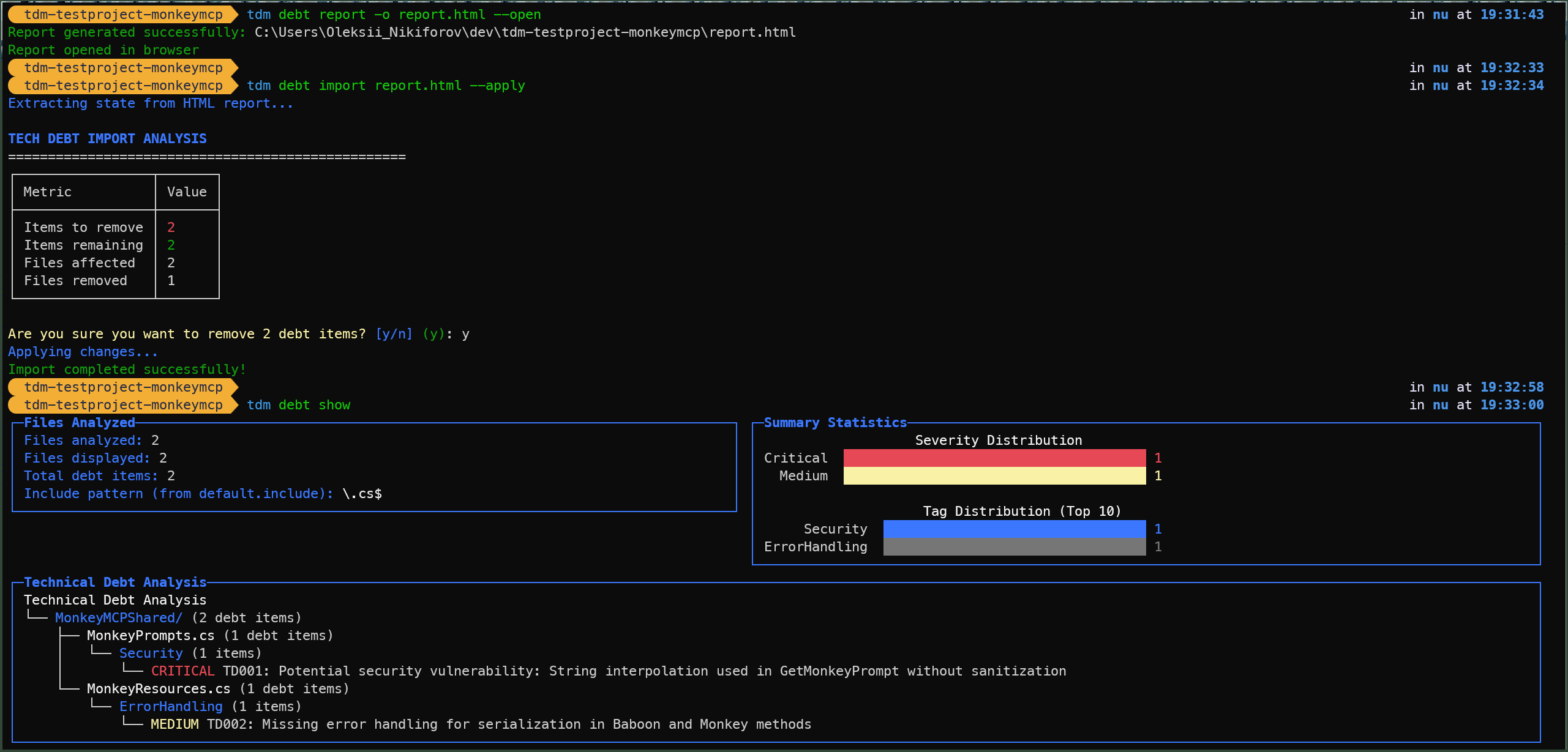
If you are not a CLI-type of person, you can use tdm debt report to open a web-based interface for managing your technical debt. The neat trick here is that you can actually save the report once you are done and import it back to tdm.
tdm debt report -o report.html --open
💡 Use tdm debt import report.html --apply to export modified report back to tdm.
Technical Debt Resolution
Now, we can use MCP integration to work on technical debt resolution. tdm provides out of the box integration/prompts for popular tools like GitHub Copilot, Claude Code, Gemini CLI.
tdm init --profile vscode --force
# √ Created .vscode/mcp.json configuration
# √ Created .github/prompts/tdm-work-on-debt.prompt.md
# √ Updated .gitignore to include .tdm folder
# √ TechDebtMaster initialization complete!
# You can now start the MCP server with: tdm mcp
This initialization command produces the necessary configuration files for integrating with the MCP server.
tdm offers complete control over agent behavior through customizable prompt files (e.g.: .github/prompts/tdm-work-on-debt.prompt.md). These files define how AI coding agents interact with your technical debt backlog via the MCP interface. You can tailor prompts to align with your team’s coding standards, preferences, and risk tolerance. This flexibility allows you to decide whether agents should automatically resolve straightforward issues or require human approval for more complex changes. The prompt-based configuration enables you to adjust the level of automation to suit different scenarios. For those feeling adventurous, you can even run a coding agent like Claude Code in “YOLO mode” with a simple prompt such as “resolve technical debt.”. The benefit of using tdm in this case is that coding agent can focus on resolving exactly technical debt you triaged previously.
For example, here is a default prompt generated during vscode profile initialization:
---
mode: agent
tools: ['changes', 'codebase', 'editFiles', 'fetch', 'findTestFiles', 'problems', 'runCommands', 'runTasks', 'search', 'searchResults', 'terminalLastCommand', 'terminalSelection', 'testFailure', 'usages', 'tdm-get-item', 'tdm-list-items', 'tdm-remove-item', 'tdm-show-repo-stats']
description: 'An autonomous workflow for identifying, analyzing, and resolving technical debt in a codebase to improve maintainability and efficiency.'
---
## Workflow
Execute the following workflow to systematically address technical debt:
### 1. Assessment Phase
- Use `tdm-show-repo-stats` to gather repository-wide technical debt metrics
### 2. Prioritization Phase
- Use `tdm-list-items` to retrieve first page of technical debt items
### 3. Verification Phase
- For each item in the list:
- Use `tdm-get-item` to fetch detailed information about the item
- Present the item to the user for review
- Ask user for confirmation to proceed with the item
### 4. Resolution Phase
- Use `tdm-get-item` to fetch detailed item information
- Present user with the item
- Analyze item validity:
- Review related code
- Verify if debt is still relevant
- Document investigation findings
- For each valid item:
- Implement necessary fixes
- Remove resolved items using `tdm-remove-item`
### 5. Validation Requirements
- Ensure all changes maintain existing functionality
- Document any architectural decisions
- Request human review for complex changes
- Once an item is resolved or is no longer relevant, remove it from the list using 'tdm-remove-item'.
🤖Let’s see it in practice:
tdm mcp
# Starting MCP server for repository: .
# Server will listen on: http://localhost:3001
# Press Ctrl+C to stop the server
# √ MCP server started successfully
And run /tdm-work-on-debt prompt for GitHub Copilot chat window:
Source code: github.com/NikiforovAll/tech-debt-master
If you have feedback, questions, or want to contribute, feel free to open an issue or pull request on GitHub.
References
- Topics:
- ai (12) ·
- ai (26) ·
- cli (10) ·
- agents (9) ·
- aspire (20) ·
- otel (1) ·
- developer-tools (8)